The Rhythm for Reading blog
Three factors to take into account when assessing reading comprehension.
28 November 2022
In the Rhythm for Reading Programme, progress in reading is measured using the Neale Analysis of Reading Ability 2nd edition revised (NARA II). Reading comprehension is one of three standardised measures in this reading assessment. There are many good assessments available, but I’ve stuck with this one because it offers three supportive features that I think are particularly helpful. If you are unfamiliar with NARA II, let me paint a picture for you. Detailed illustrations accompany each passage of text. For a child grappling with unfamiliar vocabulary or weak decoding, the illustrations offer a sense of context and I’ve seen many children’s eyes glance over to the illustration, when tackling a tricky word.
In practice, children come out of class one at a time for individual reading assessment. Each reading assessment lasts twenty minutes on average. The main advantage of an individual assessment over a group assessment is that the assessor is permitted to prompt the child if they get stuck on a word. In fact the assessor can read the tricky word after five seconds have elapsed, which helps the child to maintain a sense of the overall narrative. This level of support is limited by the rigour of the assessment. For example, an assessor would not give the definition of a word if a child asked what it meant and sixteen errors in word accuracy on a single passage of text signals the end of the assessment.
This particular individual format is more sensitive that all others in my opinion, because it minimises the influence of three cognitive factors on the scores.
Factor one: There is minimal cognitive loading of working memory as the child can refer back to the text when answering questions. In other words, they do not need to remember the passage of text, whilst answering the questions. This approach prevents a conflation between a test of comprehension and a test of working memory. Children may score higher on NARA II if working memory is likely to reach overload in other reading test formats, for example, if the child is required to retain the details of the text whilst answering comprehension questions.
Factor two: There is no writing involved in NARA II, so a child with a weak working memory achieves a higher score on the NARA II than on other formats if writing in sentences is a specific area of difficulty for them.
Factor three: The assessor keeps the child focussed on the text. This makes a big difference if a child is likely to ‘zone out’ frequently and to experience scattered or fragmented cognitive attention. In this instance, a child with weak executive function is more likely to achieve a higher score on the NARA II than on other formats, because of the support given to scattered or fragmented attention.
At the end of the ten weeks of our reading intervention, children have achieved higher scores not only in NARA II, but also in the New Group Reading Test and the Suffolk Reading Scales. Many children experience gains in cognitive control as well as reading fluency and comprehension.
Rhythm, flow, reading fluency and comprehension
20 November 2022In extant societies that live as hunter-gatherers, loud communal singing and drumming creates the illusion of a large coherent entity, large enough to deter big cats that predate on the darkest of nights. Arguably, communal singing through the night may be a key human survival strategy. There’s evidence to show that feelings of cooperation and safety are experienced when humans sing and dance together and many people report being able to sustain hours of music making, when in a group. Other species such as birds and fish deter predators by forming a large mass of synchronised movement patterns. Murmurations form before birds roost for the night and shoals of herrings achieve the same mesmeric effect when they are pursued by predators such as sea bass.
Detecting rhythm and moving in time creates a trance-like state, which allows the perception of time to shift such that the focus narrows onto staying in time with the beat of others, nearby. Anticipating what will happen next is a key element of this narrow focus. If we break that down, it involves anticipating the regularity of the beat, whether within simple or complex rhythmic patterns.
Reading for pleasure can be framed as a social situation in which the reader synchronises with the writer’s style. To ‘get into a book’ we need to achieve a flow state - which is a trance-like state resulting in relatively narrow focus. This means everything else, but the book (or screen) disappears from our attention. The entranced state induces reading fluency and comprehension, drawing us deeper into the text where we might feel that we have ‘escaped’. To escape into a book means to suspend our usual sense of who we are, having become engrossed with the text, perhaps by empathising with the characters, or simply by synchronising with the flow of the writing. A close level of synchrony between the words on the page, and our anticipation of what comes next is arguably similar to the defensive mechanism of creating a larger entity in real time because it involves losing the usual sense of self and becoming part of something larger than day-to-day life - which brings us all the way back to communal singing and dancing.
Sensitivity to rhythm is all around us
14 November 2022A few weeks ago, in an inset session at a wonderful school with beautiful inclusive approaches in their group teaching, I mentioned that rats have the same limbic structures as humans. The limbic system is the part of the brain that deals with our mammalian instincts. These keep us in tune with social information, such as social status and hierarchy, protecting and nurturing our children, bonding with sexual partners and managing affiliation. It’s a logical assumption that if we share these limbic structures, rats like humans should be able to keep time with a musical beat - or their equivalent of that. So, it was no surprise to learn that Japanese researchers have shown that rats can indeed bob along and keep time with a musical beat.
It was back in the 1980s, when American scientists first discovered the genes that determined the rhythm of the mating song of fruit flies. If we think of rhythm as a musical trait exclusive to humans, these findings in rats and flies are simply amusing, novel or entertaining. On the other hand, the bigger picture behind these findings would suggest that the natural world is inherently structured by environmental and behavioural patterns organised by rhythm. If we think of rhythm as a system of ratios, proportions and repetition, then the math of rhythm is obvious. There are cycles and rhythmic flows in tides and weather systems and indeed, migration patterns follow these cycles. In individual organisms, as well as in shoal, pod, flock and herd movement, rhythmic patterns underpin locomotion and communication. Even a human infant’s stepping reflex is organised around the inherent rhythmic systems that we share with many other species.
We humans are particularly happy when our stylised rhythms achieve a hypnotic effect, for example in Queen’s ‘We will rock you,’ - one of the songs used by the Japanese scientists to detect the sensitivity to rhythm in rats. Halfway through the Rhythm for Reading programme, this same rhythmic pattern appears and is always greeted with enthusiasm by teachers and children as a fun part of the reading intervention. Look out for the next post, which explains the connection between hypnotic rhythm, flow states, reading fluency and reading comprehension.

When Rhythm and Phonics Collide Part 2
11 November 2022In my last post I described a typical challenge facing a child with poor phonological awareness. Using a rapid colour naming test (CToPP2), it’s possible to identify that a weakness in processing the smallest sounds of language often occurs at the onset of a phoneme, in other words the onset of a syllable. Consonant blends and consonant digraphs are more affected, so, conflation between ‘thr’ and ‘fr’, or ‘cl’ and ‘gl’ is likely to happen and to impede the development of reading with ease and fluency.
The notion that sensitivity to both rhythm and the smallest sounds of language overlap in terms of data has been around for decades. A positive correlation between sensitivity to rhythm and phonemic sensitivity has been shown in many studies. It’s easy to understand that rhythm and phonological processing overlap if we consider that the start of a phoneme - the onset of a syllable is exactly where sensitivity to rhythm is measured - whether that’s the start of a musical sound or a spoken utterance.
Thinking for a moment about words that begin with a consonant, imagine focussing mostly on the vowel sound of each syllable, without being able to discern the shape of the initial phoneme with sufficient clarity. The sounds would merge together into a kind of ambient speech puddle.
Vowel sounds carry interesting information such as emotion, or tone of voice. They are longer (in milliseconds) and without defined edges. Now imagine focussing on the onset of those syllables. The consonants are shorter (in milliseconds), more sharply defined and more distinctive, leaving plenty of headspace for cognitive control. If consonants are prioritised, information flows easily and the message lands with clarity.
The Rhythm for Reading programme addresses these distinctions through group teaching that is fun and supports early reading in particular. Information processing is enhanced by sensitivity to rhythm because rhythm focusses attention onto the onset of the sound, which is where the details are sharpest. This kind of information processing remain effortless, easy and fluent.
If you’d like to know a little more about this, the details are summarised in a free infographic. Click here.

When Rhythm & Phonemes Collide
7 November 2022
Have you ever taught a child with weak phonological awareness? The differences between sounds are poorly defined and individually sounds are swapped around. A lack of phonological discrimination could be explained by conflation. Conflation, according to the OED is the merging of two or more sets of information, texts, sets of ideas etc into one.
One of the most fascinating aspects of conflation is that it can happen at different levels of conscious awareness. So, for example teenagers learning facts about physics might conflate words such as conduction and convection. After all, these terms look similar on the page and are both types of energy transfer.
Younger children might conflate colours such as black and brown as both begin with the same phoneme and are dark colours. The rapid colour naming test in the Comprehensive Test of Phonological Processing reveals such conflation. For instance, a child I assessed once as part of a reading intervention conflated brown and green. Any brown or green square in the assessment was named ‘grouwn’ (it rhymed with brown). She had conflated the consonant blends of ‘br’ and ‘gr’ and invented a name for both colours.
In the early stages of reading, conflation can underpin confusion between consonant digraphs such as ‘ch’ and ‘sh’. Another typical conflation is ‘th’, and ‘ph’ (and ‘f’). In all of these examples, the sounds are similar and they differ only on their onset - the very beginning of the sound.
A child with sensitivity to rhythm is attuned to the onsets of the smallest sounds of language. In terms of rhythmic precision, the front edge of the sound is also the point at which the rhythmic boundary occurs. Children with a well-developed sensitivity to rhythm are also attuned to phonemes and are less likely to conflate the sounds. Logically, cultivating sensitivity to rhythm would help children to detect the onsets of phonemes at the early stages of reading. Stay tuned for Part 2 and a free infographic..
Empowering children to read musical notation fluently
4 November 2022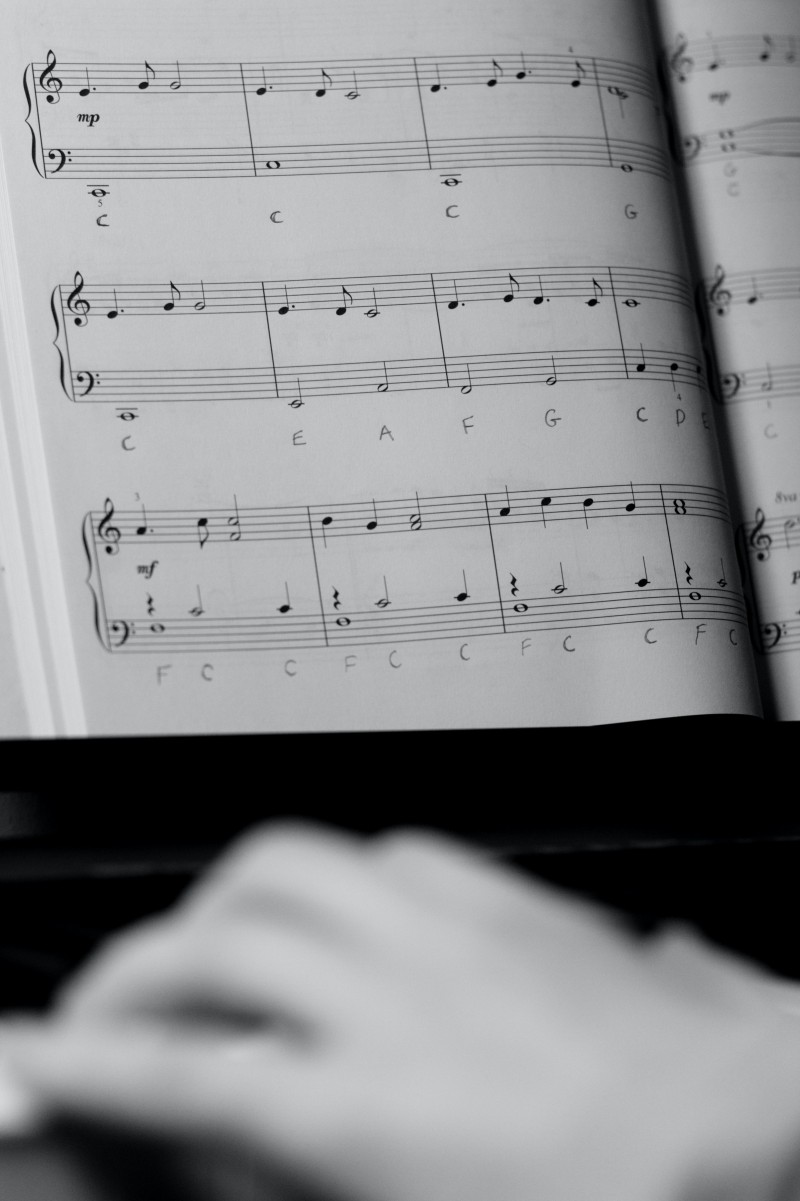
Schools face significant challenges in deciding how best to introduce musical notation into their curriculum. Resources are already stretched. Some pupils are already under strain because they struggle with reading in the core curriculum. The big question is how to integrate musical notation into curriculum planning in a way that empowers not only the children, but also the teachers.
The tried and tested ways of teaching musical notation are best suited to pupils who process information with ease. Traditionally, piano teachers begin with mnemonics for the notes that sit on the lines of the stave EGBDF (Every Good Boy Deserves Favour) GBDFA (Good Boys Deserve Fun Always) and for the notes that sit on the spaces FACE (Face) and ACEG (All Cows Eat Grass). Many teachers use these mnemonics to introduce a series of line notes and / or space notes all at once, which creates a heavy cognitive load.
What about all the children who struggle to process information, reading with ease and fluency?
Well-intentioned efforts to adapt musical notation for children who struggle to process the mnemonics, involve adding more information and increasing the cognitive load.
What is going on here?
Music teachers want children to enjoy making music and to have fun producing sounds on their instruments and they hope that in time, reading notation will gradually become familiar and easier to read. Until that point, music teachers add extra information to remind the child of the letter names of the notes. In the same vein, they often add numbers representing the finger patterns, to remind the child how to produce sounds on the instrument.
Soon enough, the page is cluttered with markings and the child has to select which ones to read.
These markings are intended as a quick fix, aiming to keep the child engaged. But of course the child relies on the letters, or the numbers, or both instead of reading the actual notes. This approach sets the child up to fail in the sense that they do not learn to read notation at all and even worse, assume that it is too difficult for them.
What could teachers do differently to support children who do not process information with ease and fluency?
A more inclusive approach would limit the cognitive load on children’s reading - which is what we do in the Rhythm for Reading Programme. Rather than teaching all the notes at once, we focus on just a few notes and develop fluency (and fun) in reading right from the start. Instead of learning the musical notes at the same time as playing musical instruments, which adds to the cognitive load, we simply use our feet, our hands and our voices, as we believe these are our most natural musical instruments.
Group learning in a structured programme supports the development of fluency, because the children are nurtured by the ethos of working together. Teamwork in combination with rhythm is an effective way to build fluency in reading, and acts as a catalyst for accelerated progress.
